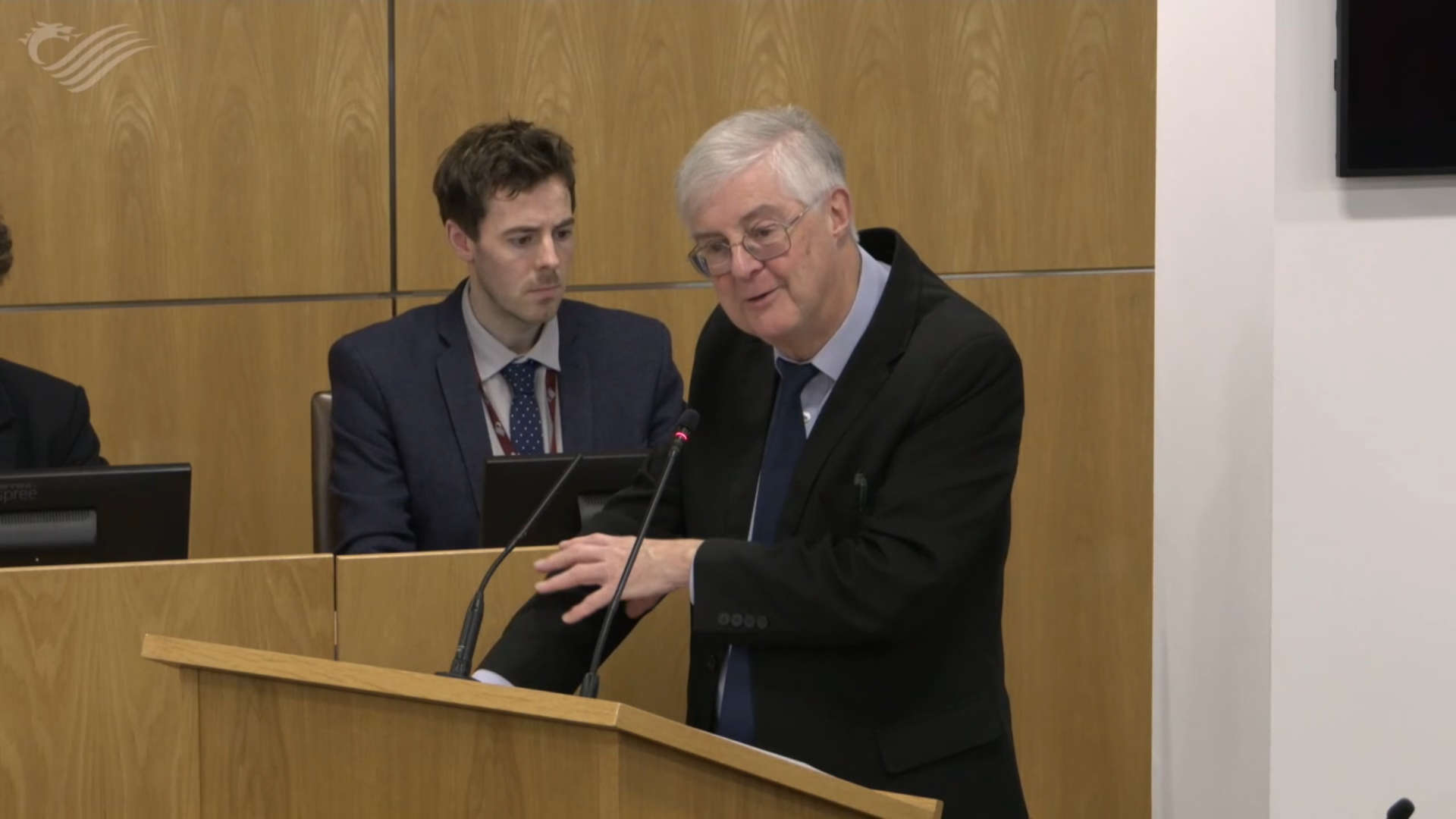
Schools in Wales will be required to deliver at least 10% of their teaching in Welsh by 2030 as part of a decade-long plan to implement “landmark” legislation.
Schools in Wales will be required to deliver at least 10% of their teaching in Welsh by 2030 as part of a decade-long plan to implement “landmark” legislation.
Mark Drakeford outlined the Welsh Government’s plan for a phased rollout of the Welsh Language and Education Act which aims to give every child “a fair chance to speak Welsh”.
Under the Act, three school categories will be created – primarily English, partly Welsh; dual language; and primarily Welsh – with targets for each for a minimum of Welsh education.
The ex-first minister, who is responsible for the language, said all schools should be given a category and provide at least 10%, 50% or 80% of teaching in Welsh by September 2030.
Prof Drakeford told the Senedd he expects “relatively few” schools to need extra time to reach the 10% minimum target, with an extension available until 2036 at the latest.
‘Trajectory’
He said the next step will be to develop a code to describe levels of Welsh language ability based on the common European framework of reference for languages or CEFR.
The Welsh language secretary said this year will also see a review of the trajectory toward reaching a million Welsh speakers and doubling daily use of the language by 2050.
Prof Drakeford explained a target of 50% of learners in Welsh-medium education by 2050 would form part of a consultation on a revised “Cymraeg 2050” strategy in 2026.
In a statement on Tuesday (October 21), he said the National Institute for Learning Welsh, or Athrofa, would be established by August 2027 to support learners of all ages.
The Athrofa will have responsibility for research and helping the education workforce, taking over and expanding on the work of the National Centre for Learning Welsh.
‘Disappointment’
The Conservatives’ Tom Giffard welcomed a detailed timeline for implementation of the Act but expressed disappointment about the lack of an education workforce plan in place.
He said Lynne Neagle, Wales’ education secretary, announced a strategic plan in a written statement at the start of the school year which contained little detail on Welsh teaching.
Prof Drakeford said the Athrofa will build on the success of the National Centre for Learning Welsh which received £4.8m this year and has now trained more than 2,000 practitioners.
Plaid Cymru’s Cefin Campbell echoed concerns about staff shortages as he called for a national plan setting out the next steps to recruit, train and retain teachers.
Mr Campbell, who was involved in developing the then-bill as part of the since-collapsed cooperation deal, said the Act’s success will depend on targets, staffing, and equal access.
He was concerned about some schools being given an extra six years to hit the 10% target.
‘Excuses’
The former lecturer said: “In Plaid Cymru's view, that should be a far shorter period because it will give too many schools an excuse not to commit to delivering that target.”
His party colleague Heledd Fychan warned: “It means that a child could be born now, depending on their postcode, who may not see any difference whatsoever, having seen this legislation passed, until they leave primary school.”
Prof Drakeford said including an extension was a response to concerns raised by schools in south-east Wales about a lack of Welsh speaking staff and time for implementation.
“I don't want to see more schools than necessary having more time,” he told the Senedd, but added it was important to give schools confidence to “come along on this journey with us”.
The former first minister concluded: “The impact of the Act goes far beyond education: it is about culture, identity and community, it is about making the language part of everyday life.”

 Vale Councillor blasts school funding in the county
Vale Councillor blasts school funding in the county
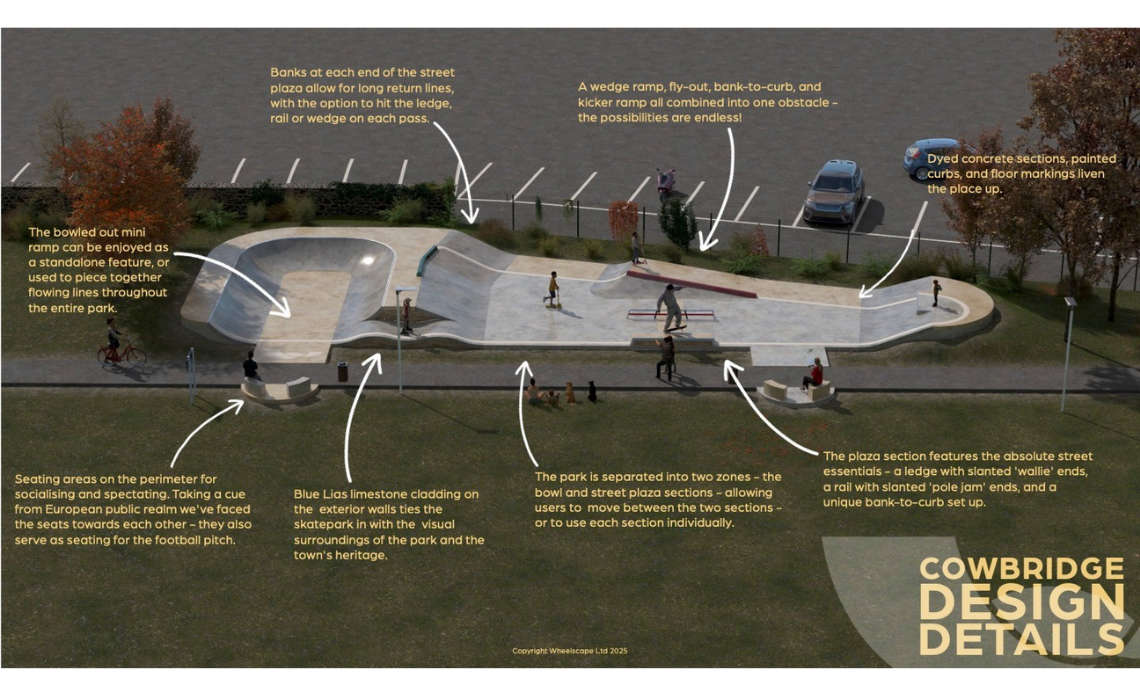 Bear Field Skate Park set for major upgrade as part of new Placemaking Plans
Bear Field Skate Park set for major upgrade as part of new Placemaking Plans
 New apprenticeship courses in construction to be introduced in Wales
New apprenticeship courses in construction to be introduced in Wales
 Former Penarth Bank could become a cafe
Former Penarth Bank could become a cafe
 New poll shows majority of Welsh voters lack voting confidence ahead of Senedd Election
New poll shows majority of Welsh voters lack voting confidence ahead of Senedd Election
 Construction hub secured for rail upgrades
Construction hub secured for rail upgrades
 Prolific thief banned from Holton Road
Prolific thief banned from Holton Road
 Cowbridge: plans for more holiday lodges
Cowbridge: plans for more holiday lodges
 Man dies suddenly in Romilly Park
Man dies suddenly in Romilly Park
 Cash boost for Sully Primary School
Cash boost for Sully Primary School
 Speed limits reduced despite objections
Speed limits reduced despite objections
 Concern over imported chicken in school meals
Concern over imported chicken in school meals
 A48 closed after three-vehicle collision
A48 closed after three-vehicle collision
 Rhys unveils red bench 'in living memory'
Rhys unveils red bench 'in living memory'
 Barry: plans lodged for 70-home development
Barry: plans lodged for 70-home development
 Plans to revamp Heritage Coast centre
Plans to revamp Heritage Coast centre
 Carnival drummers join pirate opera encore
Carnival drummers join pirate opera encore